Trumpet Schwarzschild solution in isotropic coordinates. More...
#include <TrumpetSchwarzschild.hpp>
Classes | |
| struct | Mass |
| struct | N |
Public Types | |
| using | options = tmpl::list< Mass, N > |
| template<typename DataType > | |
| using | DerivLapse = ::Tags::deriv< gr::Tags::Lapse< DataType >, tmpl::size_t< volume_dim >, Frame::Inertial > |
| template<typename DataType > | |
| using | DerivShift = ::Tags::deriv< gr::Tags::Shift< DataType, volume_dim >, tmpl::size_t< volume_dim >, Frame::Inertial > |
| template<typename DataType > | |
| using | DerivSpatialMetric = ::Tags::deriv< gr::Tags::SpatialMetric< DataType, volume_dim >, tmpl::size_t< volume_dim >, Frame::Inertial > |
| template<typename DataType > | |
| using | tags = tmpl::list< gr::Tags::Lapse< DataType >, ::Tags::dt< gr::Tags::Lapse< DataType > >, DerivLapse< DataType >, gr::Tags::Shift< DataType, volume_dim >, ::Tags::dt< gr::Tags::Shift< DataType, volume_dim > >, DerivShift< DataType >, gr::Tags::SpatialMetric< DataType, volume_dim >, ::Tags::dt< gr::Tags::SpatialMetric< DataType, volume_dim > >, DerivSpatialMetric< DataType >, gr::Tags::SqrtDetSpatialMetric< DataType >, gr::Tags::ExtrinsicCurvature< DataType, volume_dim >, gr::Tags::InverseSpatialMetric< DataType, volume_dim > > |
 Public Types inherited from gr::AnalyticSolution< 3_st > Public Types inherited from gr::AnalyticSolution< 3_st > | |
| using | DerivLapse = ::Tags::deriv< gr::Tags::Lapse< DataType >, tmpl::size_t< volume_dim >, Frame > |
| using | DerivShift = ::Tags::deriv< gr::Tags::Shift< DataType, volume_dim, Frame >, tmpl::size_t< volume_dim >, Frame > |
| using | DerivSpatialMetric = ::Tags::deriv< gr::Tags::SpatialMetric< DataType, volume_dim, Frame >, tmpl::size_t< volume_dim >, Frame > |
| using | tags = tmpl::list< gr::Tags::Lapse< DataType >, ::Tags::dt< gr::Tags::Lapse< DataType > >, DerivLapse< DataType, Frame >, gr::Tags::Shift< DataType, volume_dim, Frame >, ::Tags::dt< gr::Tags::Shift< DataType, volume_dim, Frame > >, DerivShift< DataType, Frame >, gr::Tags::SpatialMetric< DataType, volume_dim, Frame >, ::Tags::dt< gr::Tags::SpatialMetric< DataType, volume_dim, Frame > >, DerivSpatialMetric< DataType, Frame >, gr::Tags::SqrtDetSpatialMetric< DataType >, gr::Tags::ExtrinsicCurvature< DataType, volume_dim, Frame >, gr::Tags::InverseSpatialMetric< DataType, volume_dim, Frame > > |
Public Member Functions | |
| TrumpetSchwarzschild (double mass, double n, const Options::Context &context={}) | |
| TrumpetSchwarzschild (const TrumpetSchwarzschild &)=default | |
| TrumpetSchwarzschild & | operator= (const TrumpetSchwarzschild &)=default |
| TrumpetSchwarzschild (TrumpetSchwarzschild &&)=default | |
| TrumpetSchwarzschild & | operator= (TrumpetSchwarzschild &&)=default |
| TrumpetSchwarzschild (CkMigrateMessage *) | |
| template<typename DataType , typename... Tags> | |
| tuples::TaggedTuple< Tags... > | variables (const tnsr::I< DataType, volume_dim, Frame::Inertial > &x, double t, tmpl::list< Tags... >) const |
| template<typename DataType , typename... Tags> | |
| tuples::TaggedTuple< Tags... > | variables (const tnsr::I< DataType, volume_dim, Frame::Inertial > &x, double t, const IntermediateVars< DataType > &vars, tmpl::list< Tags... >) const |
| void | pup (PUP::er &p) |
| double | mass () const |
| double | n () const |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static constexpr size_t | volume_dim = 3 |
| static constexpr Options::String | help |
 Static Public Attributes inherited from gr::AnalyticSolution< 3_st > Static Public Attributes inherited from gr::AnalyticSolution< 3_st > | |
| static constexpr size_t | volume_dim |
Detailed Description
Trumpet Schwarzschild solution in isotropic coordinates.
Details
This solution is a trumpet Schwarzschild black hole in the isotropic coordinates. It is a time-independent puncture solution in 1+log slicing. The solution cannot be written down analytically in Schwarzschild coordinates or isotropic coordinates. Refer to [94] for equations and details.
We first set up a source grid in isotropic radial coordinate r, on which we compute the lapse and Schwarzschild radial coordinate R. The lapse is computed by solving eq. (54)-(56) using the toms748 algorithm, where the integrals in eq. (54)-(56) are evaluated by a tanh_sinh integrator.
Eq. (54) is for \(\alpha < \alpha_s=0.1\):
\begin{equation*} r(\alpha) = R(\alpha_s)^{(1/\alpha_s)} \exp \left[ - \int_{\alpha}^{\alpha_s} \frac{1}{\bar{\alpha} R(\bar{\alpha})} \frac{dR}{d\alpha}(\bar{\alpha}) \: d\bar{\alpha} - C_0 \right], \end{equation*}
where eq. (55) gives
\begin{equation*} C_0 = \int_{\alpha_s}^{1} \frac{\ln R(\alpha)}{\alpha^2} d\alpha. \end{equation*}
Eq. (56) is for \(\alpha > \alpha_s=0.1\):
\begin{equation*} r(\alpha) = R(\alpha)^{(1/\alpha)} \exp \left[ \int_{\alpha_s}^{\alpha} \frac{\ln R(\bar{\alpha})}{\bar{\alpha}^2} d\bar{\alpha} - C_0 \right]. \end{equation*}
A standard Gauss quadratures will fail due to singular behaviors of the integrands near the integration limits. The Schwarzschild R is then computed by solving eq. (39) using again the toms748 algorithm.
\begin{equation*} \alpha^2 = 1 - \frac{2M}{R} + \frac{C(n)^2 e^{2 \alpha / n} }{R^4}. \end{equation*}
Note that for a value of n near 2 (corresponding to standard 1+log slicing), eq. (39) has two positive roots for a fixed lapse in [0., 1.). See the following plot by Mathematica. We choose
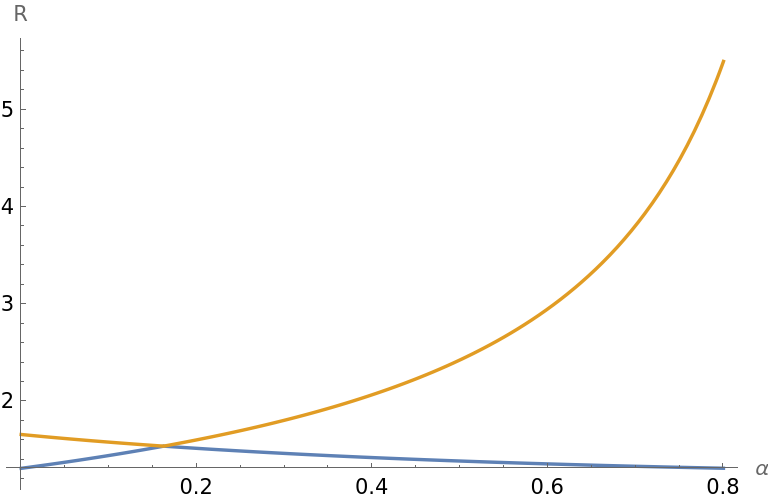
the physical root, i.e. with the correct asymptotic behaviors: R diverges as \(\alpha\) tends to 1, and R tends to the smaller solution as \(\alpha\) tends to 0.
The physical root is numerically selected by finding the critical lapse and critical Schwarzschild R, below which we tell the toms748 solver to find a root \(R\in\) [min_schwarzschild_r, crit_schwarzschild_r] or else we find a root \(R\in\) [crit_schwarzschild_r, max_schwarzschild_r]. min_schwarzschild_r is currently selected to be 0., and max_schwarzschild_r is at least as large as max_isotropic_r (currently 5000M), the maximum coordinate radius we support for this initial data. In case the solver is asked to find a Schwarzschild R greater than the max_isotropic_r, we use double the asymptotic solution from eq. (39), i.e. \(4/(1-\alpha^2)\), as solver upper bound. This latter upper bound is necessary since the integrator in eq. (55) needs lapse very close to 1 to converge.
After acquiring the lapse and Schwarzschild R, we can assemble all the 3+1 quantities in the isotropic coordinates on the source grid.
Since the user supplies grid points in the Cartesian version of the isotropic coordinates, we compute a user grid in the isotropic radial coordinate based on the Cartesian grid, compute the lapse and Schwarzschild R on the source grid, interpolate to the user grid, and then assemble all 3+1 quantities on the user grid and transform them back to the Cartesian grid.
To insulate our implementation from different mass parameters, we nondimensionalize the above process using the black hole mass until the final step of computing 3+1 quantities on the Cartesian grid, where we restore the correct unit.
The following are input file options that can be specified:
- Note
- N=2. is strongly suggested, as this gives a stationary solution in the standard 1+log slicing. The other values of N near 2. should work but have not been tested thoroughly. N outside of [2., 3.] has not been tested at all.
Some quantities very close to the puncture (<1.e-4 in isotropic radius) may have larger truncation errors. This is expected since some quantities such as the determiant of the spatial metric diverges at the puncture.
Member Data Documentation
◆ help
|
staticconstexpr |
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- src/PointwiseFunctions/AnalyticSolutions/GeneralRelativity/TrumpetSchwarzschild.hpp